By Thalif Deen
NEW YORK 17 June 2024 (IDN)—The role of nuclear weapons in world politics is taking an increasingly dangerous trend due primarily to two reasons: the ongoing military conflicts and the growing modernization of nuclear arsenals.
In the ongoing war in Ukraine, the on-again, off-again nuclear threats have come from Russia and in the conflict in Gaza, the threats have come both from right wing Israeli politicians and at least two pro-Israeli US Congressmen.
In a report released June 17, the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) warns that the role of nuclear weapons keeps growing as geopolitical relations deteriorate worldwide.
In its annual assessment of the state of armaments, SIPRI says the nine nuclear-armed states—the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan, the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North Korea) and Israel—continued to modernize their nuclear arsenals and several deployed new nuclear-armed or nuclear-capable weapon systems in 2023
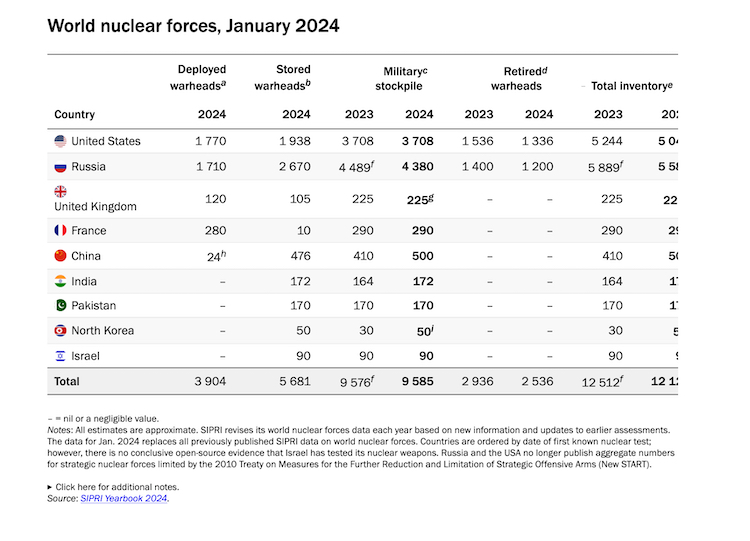
Of the total global inventory of an estimated 12,121 warheads in January 2024, about 9,585 were in military stockpiles for potential use (see the table below). An estimated 3,904 of those warheads were deployed with missiles and aircraft—60 more than in January 2023—and the rest were in central storage.
Around 2,100 of the deployed warheads were kept in a state of high operational alert on ballistic missiles. Nearly all of these warheads belonged to Russia or the US, but for the first time China is believed to have some warheads on high operational alert, said SIPRI.
“While the global total of nuclear warheads continues to fall as cold war-era weapons are gradually dismantled, regrettably, we continue to see year-on-year increases in the number of operational nuclear warheads,” said SIPRI Director Dan Smith. “This trend seems likely to continue and probably accelerate in the coming years and is extremely concerning.”
India, Pakistan and North Korea are all pursuing the capability to deploy multiple warheads on ballistic missiles, something Russia, France, the UK, the USA and—more recently—China already have.
This would enable a rapid potential increase in deployed warheads, as well as the possibility for nuclear-armed countries to threaten the destruction of significantly more targets.
Russia and the US together possess almost 90 per cent of all nuclear weapons. The sizes of their respective military stockpiles (i.e. useable warheads) seem to have remained relatively stable in 2023, although Russia is estimated to have deployed around 36 more warheads with operational forces than in January 2023.
Transparency regrading nuclear foces has declined
SIPRI said Transparency regrading nuclear foces has declined in both countries in the wake of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, and debates around nuclear-sharing arrangements have increased in saliency.
Notably, there were several public claims made in 2023 that Russia had deployed nuclear weapons on Belarusian territory, although there is no conclusive visual evidence that the actual deployment of warheads has taken place.
In addition to their military stockpiles, Russia and the USA each hold more than 1,200 warheads previously retired from military service, which they are gradually dismantling.
In a detailed analysis, Tariq Rauf, former Head of Verification and Security Policy at the Vienna-based International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), told IDN SIPRI has once again produced its authoritative assessment of world nuclear forces.
“It is not surprising that among SIPRI’s findings is that the role of nuclear weapons as well as States dependent on nuclear weapons both have increased over the past year. Many experts have commented that the risk of accidental nuclear war now is higher than during the Cold War.”
In this context, he said, it is extremely worrisome that there is no engagement on nuclear arms control between Russia and the United States, and both countries have suspended implementation of the sole remaining nuclear arms limitation treaty between them — the New START Treaty which shall expire on 5 February 2026.
There is no certainty that by April-May 2026 when the next nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) review conference opens at the UN in New York, a new treaty will be in place — the first time in the 50+ year history of the NPT that the two nuclear superpowers will be unconstrained by any strategic arms limitation treaty, he pointed out.
Under New START, each side is restricted to 1,550 deployed nuclear warheads; but if the treaty expires the two sides each could easily double or triple the number of deployed nuclear warheads on existing strategic nuclear delivery systems.
Fears of a nuclear war over Ukraine
Furthermore, the two candidates for US president both reportedly are demonstrating signs of mental deterioration which does not bode well as in the US system the president has ultimate and sole authority to launch nuclear strikes.
Statements by Russia’s leaders on possible use of nuclear weapons have created fears of a nuclear war over Ukraine, said Rauf.
The SIPRI press release makes an interesting comment that “there is no conclusive visual evidence that the actual deployment of warheads has taken place” by Russia in Belarus.
Another surprising comment by SIPRI is that ” China could potentially have at least as many intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) as either Russia or the USA by the turn of the decade, although its stockpile of nuclear warheads is still expected to remain much smaller than the stockpiles of either of those two countries.”
This seems to be at odds with the US defence department’s (DoD) statements that “the PRC possessed more than 500 operational nuclear warheads as of May 2023″ and that “DoD estimates that the PRC will probably have over 1,000 operational nuclear warheads by 2030″*and 1,500 nuclear warheads by 2035. [*Military and Security Developments Involving the People’s Republic of China 2023, US DoD.)
Furthermore, SIPRI states that “China could potentially have at least as many intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) as either Russia or the USA by the turn of the decade.”
This claim needs further elaboration and evidence, as both Russia and the US each have nearly 800 deployed and non-deployed strategic nuclear delivery vehicles (intercontinental ballistic missiles, heavy bombers).
While there was some engagement between senior military leaders of China and the US at the recently concluded Shangri-La Dialogue in Singapore, as yet the two sides have not engaged on strategic nuclear weapons, said Rauf.
The so-called dialogue between the “Permanent-5″ members of the UN Security Council (P-5 Dialogue), currently chaired by Russia, and by China from August this year, reportedly has been discussing nuclear risk reduction and nuclear doctrines but the sides remain far apart on key issues.
Regrettably, the three Western nuclear armed powers reportedly have not ceased putting pressure on countries to not sign or not ratify the 2017 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW), which currently has 93 signatories but only 70 ratifications,” declared Rauf.
China could potentially have at least as many intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) as either Russia or the USA
Meanwhile, SIPRI’s estimate of the size of China’s nuclear arsenal increased from 410 warheads in January 2023 to 500 in January 2024, and it is expected to keep growing. For the first time, China may also now be deploying a small number of warheads on missiles during peacetime.
Depending on how it decides to structure its forces, China could potentially have at least as many intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) as either Russia or the USA by the turn of the decade, although its stockpile of nuclear warheads is still expected to remain much smaller than the stockpiles of either of those two countries.
‘China is expanding its nuclear arsenal faster than any other country,’ said Hans M. Kristensen, Associate Senior Fellow with SIPRI’s Weapons of Mass Destruction Programme and Director of the Nuclear Information Project at the Federation of American Scientists (FAS).
“But in nearly all of the nuclear-armed states there are either plans or a significant push to increase nuclear forces.”
Although the UK is not thought to have increased its nuclear weapon arsenal in 2023, its warhead stockpile is expected to grow in the future as a result of the British government’s announcement in 2021 that it was raising its limit from 225 to 260 warheads.
The government also said it would no longer publicly disclose its quantities of nuclear weapons, deployed warheads or deployed missiles.
In 2023 France continued its programmes to develop a third-generation nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN) and a new air-launched cruise missile, as well as to refurbish and upgrade existing systems, according to SIPRI.
“India slightly expanded its nuclear arsenal in 2023. Both India and Pakistan continued to develop new types of nuclear delivery system in 2023. While Pakistan remains the main focus of India’s nuclear deterrent, India appears to be placing growing emphasis on longer-range weapons, including those capable of reaching targets throughout China”.
North Korea continues to prioritize its military nuclear programme as a central element of its national security strategy. SIPRI estimates that the country has now assembled around 50 warheads and possesses enough fissile material to reach a total of up to 90 warheads, both significant increases over the estimates for January 2023.
While North Korea conducted no nuclear test explosions in 2023, it appears to have carried out its first test of a short-range ballistic missile from a rudimentary silo. It also completed the development of at least two types of land-attack cruise missile (LACM) designed to deliver nuclear weapons.
“Like several other nuclear-armed states, North Korea is putting new emphasis on developing its arsenal of tactical nuclear weapons,” said Matt Korda, Associate Researcher with SIPRI’s Weapons of Mass Destruction Programme and Senior Research Fellow for the Nuclear Information Project at the Federation of American Scientists.
Major setbacks in nuclear arms control and disarmament diplomacy
“Accordingly, there is a growing concern that North Korea might intend to use these weapons very early in a conflict.”
Israel—which does not publicly acknowledge possessing nuclear weapons—is also believed to be modernizing its nuclear arsenal and appears to be upgrading its plutonium production reactor site at Dimona.
Tensions over Ukraine and Gaza wars further weaken nuclear diplomacy.
Nuclear arms control and disarmament diplomacy suffered more major setbacks in 2023. In February 2023 Russia announced it was suspending its participation in the 2010 Treaty on Measures for the Further Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms (New START)—the last remaining nuclear arms control treaty limiting Russian and US strategic nuclear forces. As a countermeasure, the USA has also suspended sharing and publication of treaty data.
In November Russia withdrew its ratification of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), citing ‘an imbalance’ with the USA, which has failed to ratify the treaty since it opened SIPRI .
‘We have not seen nuclear weapons playing such a prominent role in international relations since the cold war,’ said Wilfred Wan, Director of SIPRI’s Weapons of Mass Destruction Programme. ‘It is hard to believe that barely two years have passed since the leaders of the five largest nuclear-armed states jointly reaffirmed that “a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought”.
An informal agreement reached between Iran and the USA in June 2023 seemed to temporarily de-escalate tensions between the two countries, which had intensified over Iran’s military support to Russian forces in Ukraine.
However, the start of the Israel–Hamas war in October upended the agreement, with proxy attacks by Iran-backed groups on US forces in Iraq and Syria apparently ending Iranian–US diplomatic efforts.
The war also undermined efforts to engage Israel in the Conference on the Establishment of a Middle East Zone Free of Nuclear Weapons and Other Weapons of Mass Destruction.
More positively, the June 2023 visit to Beijing by the US secretary of state, Antony Blinken, seems to have increased space for dialogue between China and the USA on a range of issues, potentially including arms control. Later in the year the two sides agreed to resume military-to-military communication. [IDN-InDepthNews]
Photo:


